As electric vehicles go mainstream, charging them isn't just about plugging into the nearest station. Behind every charge is a digital handshake, a complex conversation between the EV, the charger, the backend system, and sometimes even the power grid. That conversation? It's powered by EV charging protocols.
In this guide, we'll unpack the four most important ones: OCPP, OCPI, OCHP, and eMIP. They're the backbone of a connected, scalable, and future-proof EV charging ecosystem.
What are EV charging standards?
EV charging, or communication, protocols allow different components of the electric vehicle charging ecosystem to “talk” to each other. They define how data is exchanged between:
- Charging stations and backend systems
- Charging networks and eMobility service providers
- Electric vehicles and energy grids
- Roaming hubs and partner networks
There are two main types of protocols:
- Hardware-level protocols
They manage physical connections with electric vehicles and in-vehicle communication (e.g., CCS, CHAdeMO, ISO 15118). - Software-level or network protocols
They manage digital communication and backend processes (e.g., OCPP, OCPI, OCHP, eMIP).
Why EV charging protocols matter
As the entire electric vehicle market accelerates, the need for seamless, reliable, and intelligent charging experiences is more critical than ever. Communication protocols form the foundation of this ecosystem, ensuring that all components of the charging infrastructure communicate seamlessly, regardless of the manufacturer, network, or location.
Interoperability
Without common communication protocols, electric vehicles would be locked into proprietary systems. Protocols like OCPP and OCPI allow hardware and software from different vendors to work together. This ensures that a charger from Brand A can be managed by a platform from Provider B and accessed by a user from Network C, all without friction.
Roaming capability
Protocols such as OCPI, OCHP, and eMIP enable drivers to charge across multiple networks with a single account or RFID card. Just like mobile roaming, these international standards allow drivers to use various charge point operators, creating a better user experience and broader infrastructure access.
Real-time data exchange
Modern EV charging relies on real-time data, charger availability, pricing updates, session tracking, and energy usage. Protocols ensure this information is shared instantly and accurately between stations, backend systems, and service providers, enabling features like dynamic pricing and remote diagnostics.
Smart charging and grid integration
Protocols like OCPP 2.0.1 and ISO 15118 enable advanced energy management features, including smart charging, load balancing, and even vehicle-to-grid (V2G) functionality. These tools are critical for grid stability as EV demand scales, allowing charge point operators to optimize based on time-of-use rates and grid load.
Scalability and future-proofing
As the EV industry grows, operators need protocols that support hundreds or thousands of units. Open standards allow plug-and-play integration of new hardware, software upgrades, and service expansions, without getting locked into a single vendor ecosystem.
Key EV charging standards
EV charging infrastructure is only as effective as the protocols that connect its various components. While physical standards like CCS or CHAdeMO govern how power flows, the communication protocols ensure everything behind the scenes works, from session management and remote monitoring to billing and roaming.
In this section, we'll break down four of the most important backend communication protocols: OCPP, OCPI, OCHP, and eMIP. Each plays a unique role in enabling interoperability, enhancing user experience, and helping operators build scalable, intelligent, and future-proof charging networks.
Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP)
The Open Charge Point Protocol(OCPP) is the most widely adopted communication standard in the EV charging world. Developed by the Open Charge Alliance, OCPP defines how EV charging stations communicate with central management systems (CPMS), essentially the backend software that monitors and controls the network.
What does OCPP do?
OCPP allows EV charging stations and backend platforms to:
- Start or stop charging sessions remotely as soon as the electric vehicle is connected
- Monitor charging status and station health
- Push firmware and software updates
- Collect detailed data on usage and energy consumption
- Enable smart charging and grid integration features
By separating the hardware (charging station) from the software (management system), OCPP gives operators the freedom to mix and match vendors, helping avoid vendor lock-in and allowing greater flexibility in scaling a charging network.
Key versions of OCPP
OCPP 1.6:
- Most commonly used today
- Supports basic smart charging, remote control, and charge session data
- JSON and SOAP support for flexible integrations
OCPP 2.0.1 (the latest stable version):
- Adds Plug & Charge support via ISO 15118
- Improved security and encryption
- Smart charging profiles and reservation systems
- Better diagnostics and event notifications
Why OCPP matters
- Open and vendor-neutral: Anyone can implement it - no licensing required
- Widely supported: Compatible with thousands of electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE) models worldwide
- Future-ready: Enables advanced use cases like V2G, load balancing, and dynamic pricing
Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI)
The Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) is a protocol designed to enable roaming and data exchange between EV charging networks. Developed by the EVRoaming Foundation, OCPI allows EMSPs and CPOs to work together, so EV drivers can seamlessly use chargers across different networks, much like mobile phone roaming.
What does OCPI do?
OCPI defines how two charging networks exchange key information, including:
- Charger locations and availability
- Real-time pricing and tariffs
- Authentication and access control (via tokens or RFID cards)
- Charging session details and billing records
In essence, OCPI enables a driver with one account or app to locate, access, and pay for charging services on multiple, unaffiliated networks, without setting up separate accounts.
How OCPI works
- Built as a modular, RESTful API
- Uses JSON for lightweight, flexible data exchange
- Supports pull and push modes for real-time updates
- Openly available and not controlled by a single company
- Roaming: Crucial for public EV charging access across regions and networks
- User-friendly: No need for multiple apps or subscriptions
- Operator-friendly: Supports automated settlement, contract management, and service level agreements
- Data-driven: Helps improve charger availability, reliability, and customer transparency
Why OCPI is important
- Simplified roaming: One connection to a clearing house = access to many networks
- Standardized integration: Reduces custom development for each partner
- Efficient scalability: Particularly beneficial in complex, multi-party environments
- Regulatory compliance: Aligns with many EU transparency and access mandates
Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP)
The Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP) is a communication standard that enables interoperability between EMSPs and CPOs through a centralized clearing house. Developed and maintained by Smartlab Innovationsgesellschaft mbH, OCHP is widely used in Europe, especially in markets like Germany, to simplify roaming and backend integration.
Unlike OCPI, which supports peer-to-peer roaming, OCHP operates via a clearing house model. In this setup, all roaming communications (authentication, pricing, billing, and charger status) flow through a central intermediary platform, making it easier to manage relationships between many parties.
OCHP allows:
- Charger availability and location sharing
- Real-time session management and CDR (Charge Detail Record) exchange
- Roaming authorization via a single interface
- Pricing and contract updates between EMSPs and CPOs
- Based on SOAP/XML architecture
- Enables both push and pull communication models
- Commonly paired with clearing house platforms like ladenetz.de
Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP)
The Open Clearing House Protocol (OCHP) is a communication standard that enables interoperability between EMSPs and CPOs through a centralized clearing house. Developed and maintained by Smartlab Innovationsgesellschaft mbH, OCHP is widely used in Europe, especially in markets like Germany, to simplify roaming and backend integration.
What does OCHP do?
Unlike OCPI, which supports peer-to-peer roaming, OCHP operates via a clearing house model. In this setup, all roaming communications (authentication, pricing, billing, and charger status) flow through a central intermediary platform, making it easier to manage relationships between many parties.
OCHP allows:
- Charger availability and location sharing
- Real-time session management and CDR (Charge Detail Record) exchange
- Roaming authorization via a single interface
- Pricing and contract updates between EMSPs and CPOs
How OCHP works
- Based on SOAP/XML architecture
- Enables both push and pull communication models
- Commonly paired with clearing house platforms like ladenetz.de
Key benefits of OCHP
- Simplified roaming: One connection to a clearing house = access to many networks
- Standardized integration: Reduces custom development for each partner
- Efficient scalability: Particularly beneficial in complex, multi-party environments
- Regulatory compliance: Aligns with many EU transparency and access mandates
eMobility Interoperation Protocol (eMIP)
The eMobility Interoperation Protocol(eMIP) is a communication standard that enables secure, trusted data exchange between EMSPs and CPOs. Developed by Gireve, a European EV roaming platform, eMIP focuses on simplifying roaming agreements, data standardization, and service validation in a multi-partner environment.
Unlike OCPI and OCHP, eMIP is not just a protocol. Gireve is part of a broader trust-based ecosystem that includes business validation, contract management, and platform-level governance.
What does eMIP do?
eMIP supports:
- Charger discovery: Real-time status, availability, and location sharing
- Session management: Start, stop, and monitor sessions across networks
- Billing and clearing: Standardized CDRs for invoicing
- Authentication: Verifies user identity and contract validity between EMSPs and CPOs
- Roaming agreements: Built-in support for managing contracts and usage permissions
How eMIP works
- Integrated tightly into the GIREVE platform, but available to other partners
- Emphasizes contractual security, certification, and business rules enforcement
- Supports data quality validation to reduce session errors and billing disputes
Benefits of eMIP
- Trusted interoperability: Only certified and approved partners can exchange data
- Business-layer integration: Beyond technical data, eMIP manages partner relationships
- Improved accuracy: Reduces roaming transaction errors through validation checks
- European compliance: Aligns with GDPR and other EU data-sharing frameworks
EV charging protocols and interoperability
Interoperability is the ability of different systems, devices, and networks to work together and communicate effectively, regardless of the manufacturer, service provider, or software platform.
It is one of the most critical challenges and opportunities in the EV charging industry. Without interoperability, EV drivers would face a fragmented ecosystem, where access, payments, and data vary across different charging networks. EV charging standards like OCPP, OCPI, OCHP, and eMIP exist to solve this very problem.
Why interoperability matters
- For EV drivers: Seamless access to chargers across multiple networks using a single RFID card or app
- For charge point operators: Freedom to work with multiple hardware vendors and service providers
- For the grid: Consistent data flow allows for smart energy management and demand response
- For businesses: Reduces vendor lock-in, supports scalability, and simplifies backend integrations
When protocols are implemented properly, EV drivers can:
- Locate and book charging stations
- Authenticate and initiate charging sessions
- Receive transparent pricing
- Get billed accurately, regardless of the network they're on
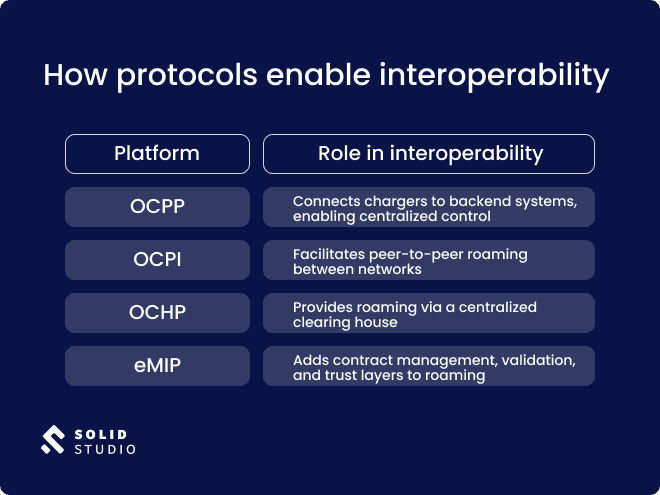
How protocols enable interoperability
Each protocol addresses a different part of the interoperability puzzle. For example:
- OCPP ensures that chargers from various manufacturers can be managed through a single software platform.
- OCPI and OCHP allow drivers to roam freely between networks.
- eMIP adds structure and security to these interactions, making them reliable and scalable.
How to build an interoperable, future-proof EV charging network
Understanding EV charging protocols is a strategic advantage. Whether you're launching a public charging network, scaling a fleet operation, or integrating roaming partnerships, the right mix of protocols will determine your network's flexibility, scalability, and long-term ROI
- Use OCPP for backend charger communication and remote management
- Use OCPI, OCHP, or eMIP to support roaming, third-party access, and billing integration
- Adopt open standards to stay agile and avoid vendor lock-in
- Prepare for the future with protocols that support smart charging, V2G, and Plug & Charge
By aligning your infrastructure with widely supported, open protocols, you're building a smarter, more connected EV ecosystem that scales with demand and innovation.
Need support in making decisions about your EV charging infrastructure?
We're here to help. Book a call with our eMobility consultants now!