As EV infrastructure expands, the real challenge isn’t just building more charge points. It’s making sure they all work together.
Different networks, providers, and platforms need a common language. That’s where the Open InterCharge Protocol (OICP) comes in.
Created by Hubject, OICP enables seamless communication between Charge Point Operators (CPOs), eMobility Service Providers (eMSPs), and backend systems. It powers real-time services like eRoaming, authorization, billing, and pricing exchange, helping unify what would otherwise be a fragmented charging landscape.
With support for over half a million charging points across 52 countries, OICP has become one of the most widely adopted EV protocols worldwide.
In this article, we’ll look at how it connects key players in the ecosystem and why it remains critical to EV adoption at scale.
What is OICP?
The Open InterCharge Protocol (OICP) is a communication standard developed by Hubject in 2012. It enables CPOs and eMSPs to exchange data through a centralized platform called the Hubject Brokering System (HBS).
By standardizing how EV charging services communicate, OICP removes the need for custom integrations between every provider, making scalable, cross-network interoperability possible.
Hubject, the company behind OICP, is a joint venture formed by leading automotive and energy companies including BMW, Bosch, Daimler, EnBW, Innogy, Siemens, and Volkswagen. From the beginning, its mission has been to streamline the EV charging landscape through open standards and shared infrastructure.
OICP supports various services, including eRoaming, session tracking, pricing, and Plug and Charge (via ISO 15118). Since 2019, the protocol has been available as open-source under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 license. This model has allowed developers and service providers to contribute to its ongoing evolution and broaden its adoption.
By acting as a universal layer between service providers and charging networks, OICP simplifies connecting systems across countries, vendors, and technologies. That’s why it’s considered one of the most widely implemented protocols in the European EV charging ecosystem and a blueprint for global scalability.
The evolution of the OICP protocol
Since its launch in 2012, the Open InterCharge Protocol has evolved through continuous versioning and modular updates. Each release has introduced improvements that reflect the needs of a growing, increasingly complex EV charging ecosystem.
OICP is designed to be flexible, so Hubject versions individual services independently, rather than releasing monolithic updates. This modular structure makes it easier for participants to adopt new features without overhauling their entire system.
The latest stable release, OICP 2.3, includes significant upgrades in several key areas:
- Improved Point of Interest (POI) data quality
- Enhanced compliance with calibration laws
- Better data performance
- Greater transparency across use cases
To support smooth adoption, Hubject provides remote testing tools that allow Charge Point Operators to validate their implementations before going live. The protocol is based on SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) and supports real-time and asynchronous operations.
While Hubject maintains a session and transaction database, it does not push data directly to charging stations. Instead, it focuses on enabling consistent, reliable exchange between backend systems. This model reinforces OICP’s role as a trusted intermediary that scales with the ecosystem rather than constraining it.
OICP for Charge Point Operators (CPOs)
For Charge Point Operators, OICP offers a streamlined way to open their infrastructure to a wider audience of EV drivers, without managing separate integrations for each service provider. By connecting to Hubject’s Brokering System via the SHARE interface, a CPO can make its network accessible to any eMobility Service Provider already on the platform.
This shared framework turns the Hubject ecosystem into a kind of open marketplace. Once a CPO is integrated, drivers with contracts through any connected eMSP can locate, authorize, and use their charging stations, all through a standardized, backend connection.
OICP handles critical processes like:
- Sharing charge point availability and status
- Exchanging session and pricing information
- Managing charging events across borders
The result is a scalable, interoperable charging infrastructure that extends reach and removes technical friction. CPOs benefit by gaining access to a large, ready-made pool of potential customers, without building and maintaining multiple bilateral integrations.
OICP for eMobility Service Providers (eMSPs)
For eMobility Service Providers, OICP offers a way to instantly extend their charging network coverage, without the burden of negotiating and integrating with individual Charge Point Operators. Through Hubject’s CONNECT interface, eMSPs can offer their customers access to a vast network of public charging stations across Europe and beyond.
Charging stations inside the Hubject ecosystem are marked with the intercharge logo, making it easy for users to identify compatible locations. From the customer’s perspective, the experience is unified even if the underlying infrastructure spans dozens of CPOs.
There are two ways an eMSP can connect to the Hubject platform:
- Online EMP: Provides full real-time communication with the Hubject Brokering System, including instant authorization and session control.
- Offline EMP: Transfers customer authentication data to Hubject in advance, allowing authorization even without a live connection.
This flexibility allows eMSPs to scale at their own pace. Even providers without advanced backend capabilities can participate in cross-network charging through OICP’s support for offline authentication. In both cases, the protocol helps streamline access, improve customer experience, and reduce integration overhead.
Services and capabilities of the OICP Protocol
OICP supports services that ensure interoperability, efficiency, and a smooth user experience across EV charging networks. They cover everything from real-time session handling to dynamic pricing and offline authentication.
Key capabilities include:
- eRoaming authorization: Enables real-time or remote start/stop authorization for charging sessions. It also manages Charging Data Records (CDRs) to ensure accurate billing between providers.
- Reservation services: Allows EV drivers to reserve charging stations in advance. The protocol handles compatibility checks and confirms bookings with the relevant CPO.
- EVSE data and status sharing: Communicates both static data (like charger location and hardware specs) and real-time availability. This ensures accurate information is presented to end users.
- Dynamic pricing: Supports flexible pricing models that vary by location, time, or energy consumed. This enables providers to reflect real-world pricing conditions within their apps and services.
- Charging notifications: Delivers status updates throughout a charging session, including start, stop, error messages, and other progress indicators.
- Authentication data exchange: Allows offline EMPs to securely transfer user credentials to Hubject, enabling charging without a live connection.
In addition, Intercharge Direct, a feature built into the OICP protocol, enables ad hoc payments. This means EV drivers without a contract can initiate and pay for charging sessions directly at participating stations, expanding accessibility for casual or one-time users.
These services work together to reduce integration friction, standardize communication, and enhance the overall reliability of cross-network EV charging.
OICP market roles and architecture
OICP defines a clear set of roles that support a connected EV charging ecosystem. By formalizing these relationships, the protocol ensures consistency in how data and services flow between all parties.
Key participants
- EV user: The driver who initiates a charging session. While not a direct user of OICP, their experience depends on how effectively the protocol connects backend systems.
- eMobility Service Provider (eMSP): Manages the customer relationship and provides access to charging services. The eMSP uses OICP to communicate with CPOs via the Hubject platform.
- Charge Point Operator (CPO): Owns and operates the physical charging infrastructure. CPOs use OICP to share real-time station data, session information, and pricing with the wider network.
- Hubject: Acts as the central eRoaming platform. The Hubject Brokering System (HBS) facilitates secure, standardized communication between all connected parties.
Aggregators and sub-partners
Both eMSPs and CPOs can integrate directly with Hubject or work through aggregators. These intermediaries handle the technical connection to OICP on behalf of smaller providers, allowing them to participate in the network without managing a full-scale integration. This approach reduces onboarding complexity and promotes broader market inclusion.
By structuring the ecosystem in this way, OICP ensures that each participant can focus on their core function while still delivering a unified experience to the EV driver.
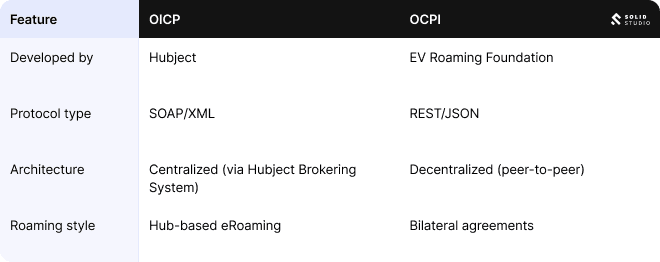
OICP vs OCPI: How do they compare?
As the EV charging industry matures, multiple open standards have emerged to support interoperability. Two of the most widely discussed are OICP and OCPI. While both aim to facilitate data exchange between eMobility Service Providers (eMSPs) and Charge Point Operators (CPOs), they take different approaches in architecture and design.
Key differences
- Architecture OICP uses a centralized model with Hubject acting as an intermediary platform. This allows for unified onboarding, testing, and service orchestration. In contrast, OCPI is decentralized, allowing CPOs and eMSPs to connect directly through bilateral agreements.
- Protocol Design OICP is built on SOAP/XML, which is well-suited for structured, enterprise-grade communication. OCPI leverages REST/JSON, which is lightweight and developer-friendly, especially for newer platforms.
- Use Case Fit OICP is often preferred by companies looking for a managed, all-in-one eRoaming environment. OCPI appeals to organizations that want more control and flexibility in peer-to-peer relationships.
Both protocols are widely adopted and continue to evolve. Many large platforms support both standards to accommodate varying partner needs.
The Role of OICP in Unifying the EV Charging Ecosystem
OICP plays a crucial role in connecting the dots across the EV charging landscape. By enabling seamless communication between CPOs, eMSPs, and platforms like Hubject, it removes integration barriers and supports scalable, cross-border charging solutions.
As the protocol continues to evolve, it remains a solid foundation for building interoperable, future-ready EV services.
Looking to integrate OICP or expand your eMobility offering?
Book a consultation with Solidstudio to explore how we can support your roadmap with the right architecture and implementation expertise.
For those who look for a more in-depth knowledge, we have published a comprehensive training covering all the technical aspects of OICP.